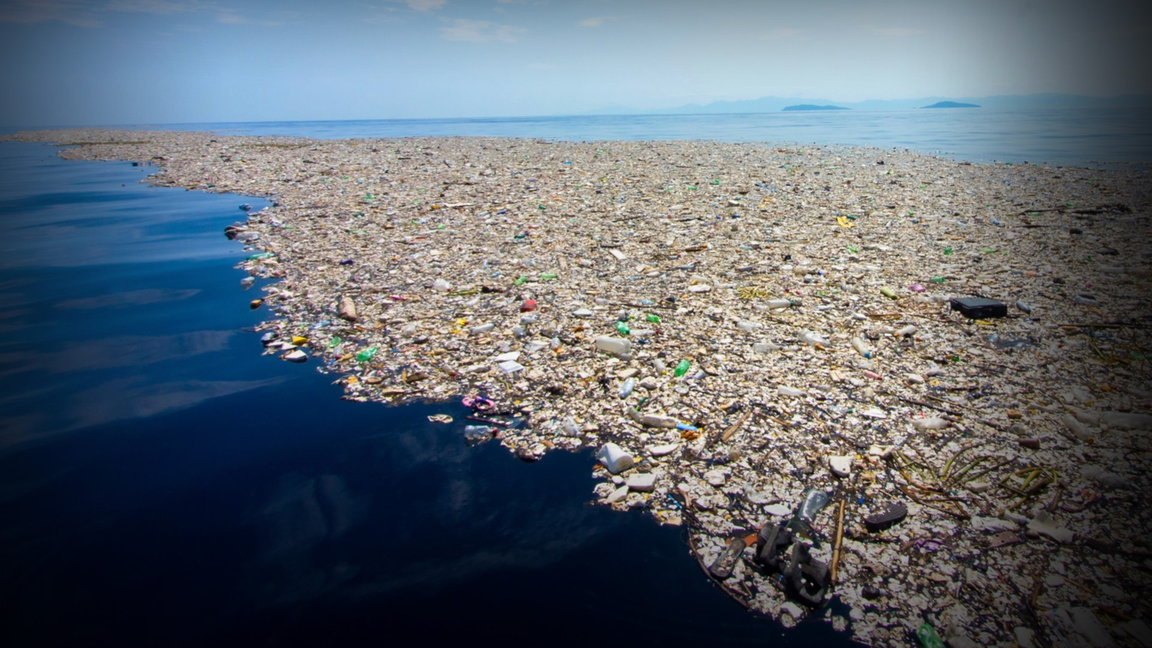
Climate change is one of the biggest risks that threatens life as we know it on earth. global emissions are rising and global targets are still far from achieving. 99% of plastics are produced from chemicals sourced from fossil fuels one of the biggest contributors to climate change Plastic the If this trend were to continue, the GHG emissions from plastics would reach 15% of the global carbon budget by 2050. The International Energy Agency says. Even as we try to curb fossil-fuel use in sectors such as transportation and heating, consumption of plastics will only increase, based on our current trajectory. The Center for International Environmental Law (CIEL) estimates that if trends continue, plastics will account for 20% of oil consumption by 2050.